Motivation:
Which display should you choose when buying a TV or laptop or mobile device, bigger size or bigger resolution?
Terminologies:
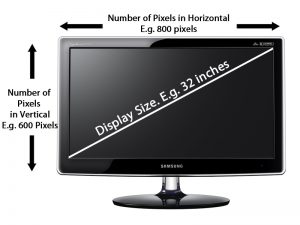
Size Display size is measured in inches. Here we only measure the diagonal size in inches and not the horizontal or vertical size of the screen.
Square the horizontal or vertical size of the screen in inches, and add the two numbers together. Find the root of that resulting number, and you have your display's diagonal in inches.
Pixel It is the smallest element that can be displayed on a screen. To be more simple, it is just a single dot on a display or a screen.
Resolution Resolution refers to size of the display in terms of pixels. E.g. Resolution of 800×600 pixels means that the there are 800 pixels horizontally and 600 pixels vertically. So therefore there are a total of 480000 pixel in the display.
Square the display's width and height in pixels, and add the two numbers together. Find the root of that resulting number, and you have your display's diagonal resolution in pixels.
Pixel Density Many of us are not aware of the importance of Pixel Density in displays. It is the thing which describes the sharpness and clarity.
Pixel Density is usually measured in PPI (Pixels Per Inch) which refers to number of pixels present per inch on the display. Higher the pixel density higher is the sharpness of the content.
Pixel Density is calculated based on the resolution and size of the display.
Pixel Density = Diagonal resolution in pixels/Diagonal in inches
Consider the above image. The alphabet “A” on the left is displayed on screen (32 inch display size) with lower resolution. The alphabet “A” on the right is displayed on the screen (32 inch display size) with higher resolution which delivers better sharpness.
What does this mean?
The thing with PPI is that with the same resolution, the larger the screen, the lower the PPI, the lower sharpness. This is because a larger screen means the individual pixels have to be larger to fill the space.
If you compare iPhone 6s Plus and Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge which both have the same size 5.5 inch but iPhone 6s Plus comes with 1920×1080 resolution at 401 PPI while Galaxy S7 Edge comes with a 2560×1440-pixel resolution at 534 PPI. It means the text and images on the Galaxy S7 Edge’s display are sharper than on the iPhone 6s Plus’ display.
The interesting thing about devices that boast a higher PPI that 400 is that your eyes can’t see the high concentration of pixels at normal smartphone viewing distances. Your naked eye can only see densities of up to 399, so you won’t be able to tell the difference between a device with a PPI of 400 and 440 (the Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge, for example).
Some examples:
- Dell XPS 13 (2016) has a pixel density of 276.
- Dell Precision 5510 Workstation 15 (2016) has a pixel density of 282.
- MacBook Pro 13-inch (2016) has a pixel density of 227.
- MacBook Pro 15-inch (2016) has a pixel density of 220.