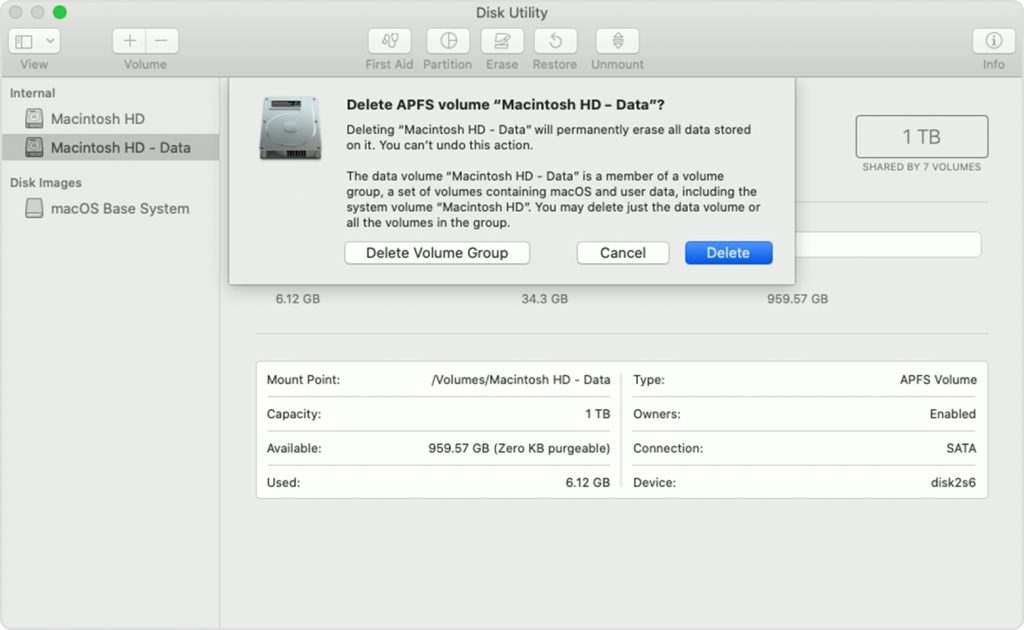
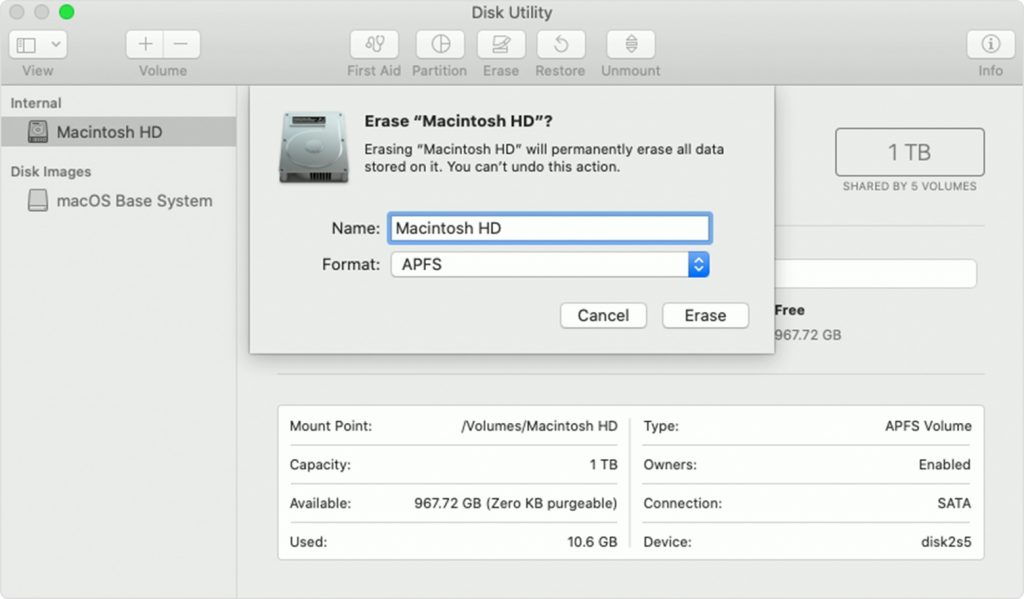
Motivation:
- You have a web application the backup of which needs to be created daily.
- You have a web application the content of which needs to be replicated daily.
- You have data folder the content of which needs to be augmented daily.
Commands:
- Copying files and folders inside one folder to another:
robocopy E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com E:\inetpub\wwwroot\backup.domain.com /e /e Copies subdirectories. This option includes empty directories. robocopy \\192.168.1.49\E\inetpub E:\inetpub /e
- Moving entire folder to another location:
PS C:\> Move-Item -path \\192.168.1.15\e\inetpub\ -destination E:\ -force where PS C:\> is PowerShell.
- Moving new files and folders inside one folder to another:
robocopy E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com E:\inetpub\wwwroot\archive.domain.com /move /e /move Moves files and directories, and deletes them from the source after they are copied.
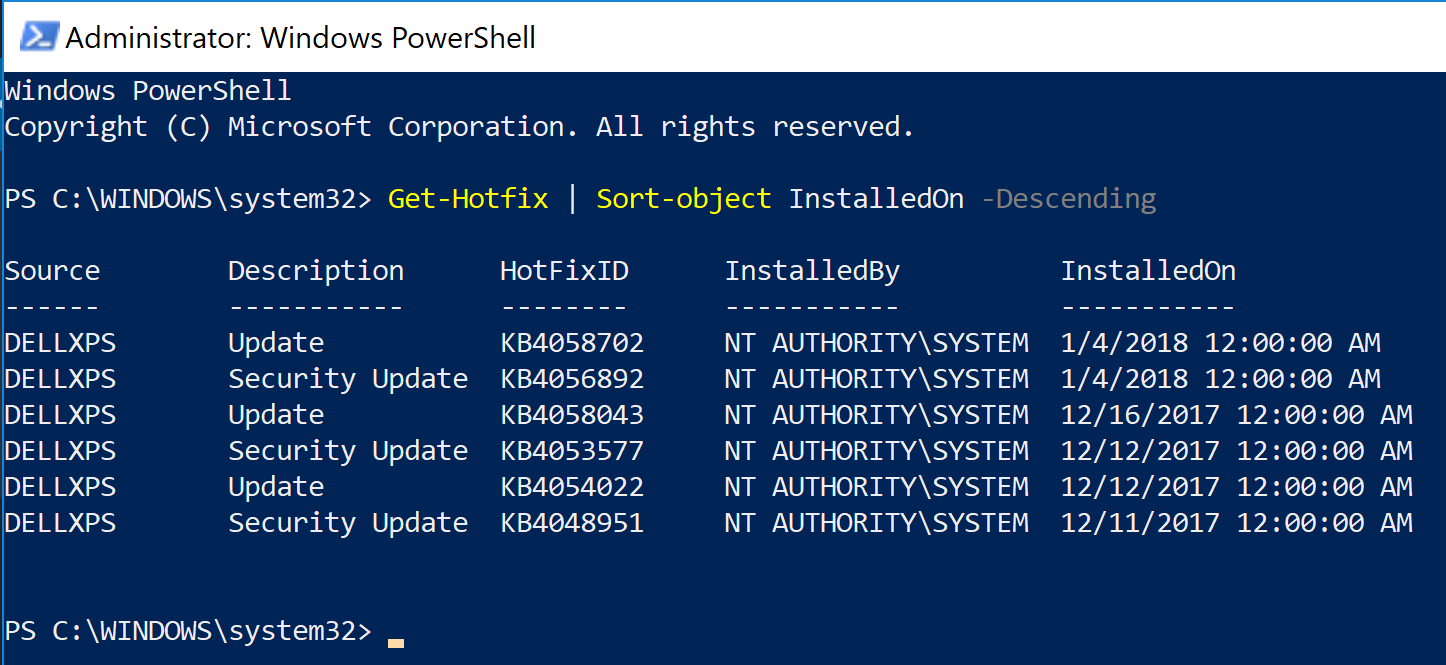
- Copying (mirroring) entire data from one drive to another, including file and folder permissions:
robocopy E:\ G:\ /MIR /COPYALL /ZB /W:1 /R:2 /XO or robocopy E:\ G:\ /TEE /LOG+:F:\robolog.txt /MIR /COPYALL /ZB /W:1 /R:2 /XO E:\ - Source folder. This can be a UNC path. G:\ - Destination folder. This can be a UNC path. /TEE - Display the output of the command in the console window and write it to a log file. /LOG+:F:\robolog.txt - Write the logs to F:\robolog.txt. The + sign means appending the content to the log file. /MIR - Copy all files and subfolders, remove files and folders from the destination if they no longer exist on the source. /COPYALL - Copy all of the NTFS permissions and attributes (security permissions, timestamps, owner info, etc.) /ZB - Use restartable mode when copying files. If a file is in use, retry after a set amount of time (see /W:1 and /R:2). If access is denied then try to copy in backup mode. /W:1 - Wait for 1 second between retries when copying files. /R:2 - The number of retries on failed copies. /XO - eXclude Older files/folders if the destination file or folder exists and has the same date. If destination file exists and is the same date or newer than the source - don't bother to overwrite it.
- Augmenting files and folders (making an incremental backup) from one drive to another, including file and folder permissions:
robocopy E:\ G:\ /E /COPYALL /ZB /W:1 /R:2 /XO /XX or robocopy E:\ G:\ /TEE /LOG+:F:\robolog2.txt /E /COPYALL /ZB /W:1 /R:2 /XO /XX /E - Copy Subfolders, including Empty Subfolders. /XX - eXclude "eXtra" files and dirs (present in destination but not source). This will prevent any deletions from the destination.
- Granting Full control to a user or group:
icacls "E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com\App_Data" /grant "IUSR":(OI)(CI)F /T icacls "E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com\App_Data" /grant "IIS_IUSRS":(OI)(CI)F /T CI - Container Inherit - This flag indicates that subordinate containers will inherit this ACE (access control entry). OI - Object Inherit - This flag indicates that subordinate files will inherit the ACE. OI and CI only apply to new files and sub-folders). F - Full Control /T - Apply recursively to existing files and sub-folders.
- Deleting and creating a folder:
rmdir "E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com\Temp\" /S /Q mkdir "E:\inetpub\wwwroot\website.domain.com\Temp\
- Recursively deleting all files in a folder and all files in its sub-folders:
cd C:\inetpub\wwwroot del /s *.log /s - delete all the files in the sub-folders. del /s /f /q *.* /f - force deletion of read-only files. /q - do not ask to confirm when deleting via wildcard.
- Recursively deleting a folder, its files and its sub-folders:
rmdir .\force-app\main\default\objects /s /q /s - delete all the files in the sub-folders.
- Enabling long paths and file names: For Windows 10, Version 1607, and Later: Open Group Policy (gpedit.msc) and go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Filesystem. Set “Enabling Win32 long paths” to “Enabled“. Restart the machine. Then use command below:
PS C:\> Move-Item -path \\192.168.101.157\e\Files\ -destination E:\ -force
- Removing a drive letter from a volume:
mountvol F: /D /D - remove the drive letter from the selected volume.